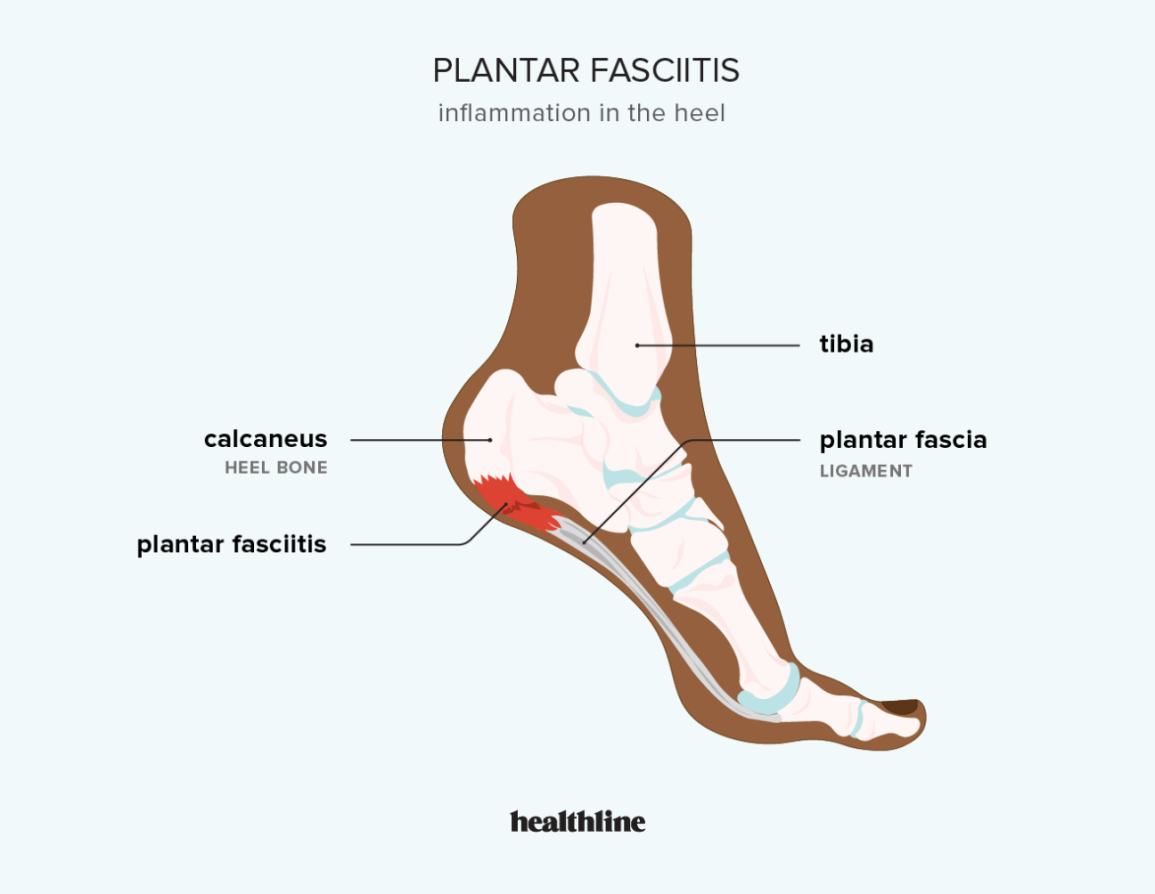
Plantar Fasciitis So Bad I Can’t Walk is a chronic irritation, tendinosis, and inflammation of the plantar fascia on the bottom of your foot. People complain of a sharp heel pain that is worse in the morning when getting out of bed. One person called it an “ice pick” though the foot every morning. Commonly it is less painful while someone is moving around but returns after resting. Plantar fasciitis commonly occurs in people who spend significant amounts of time standing or walking.
The plantar tendon runs from your heel toward the ball of your foot. When standing, the tendon is stretched and stress is placed on it. Walking, running or jumping places increased stress on the tendon.
Stress causes inflammation, damage, and scar tissue to build up, further injuring the tendon. The injury will continue through periods of improvement and aggravation. It commonly effects people for many months, limiting their daily activities.
Plantar fasciitis usually occurs from overuse, increased pounding, standing, walking, running, or bad shoes. All of these activities overwhelm the tissue on the bottom of the foot. However, it also overwhelms the other muscles in the foot and lower leg. People with plantar fasciitis usually have muscle spasms and small injuries in their lower leg muscles and feet in addition to the plantar fasciitis. The muscle spasms further change foot and ankle mechanics, making it less likely to walk and run with a smooth and efficient gait. The muscles restrict movements increasing the foot pounding on the pavement, further aggravating the plantar fasciitis.
Massage therapy address the muscle spasms, tenderness, loss of flexibility, and trigger points in all of the lower leg muscles. Getting the lower leg muscles to heal helps protect the plantar fasciitis and speeds your recovery.
The lower legs muscles work with the foot muscles to absorb the pounding forces of walking and running. If the leg muscles are injured, they will not abosrb the impact forces with each step. We have found treatment that combines massage therapy with traditional physical therapy decrease people’s pain and overall recovery times. Massage therapy can address the muscle spasms, tenderness, hypertonicity, and trigger points of the gastrocs, soleus, tibialis anterior, tibials posterior, hamstrings, and quadricep muscles. When these muscles are functioning they reduce the strain on the bottom of the foot.
